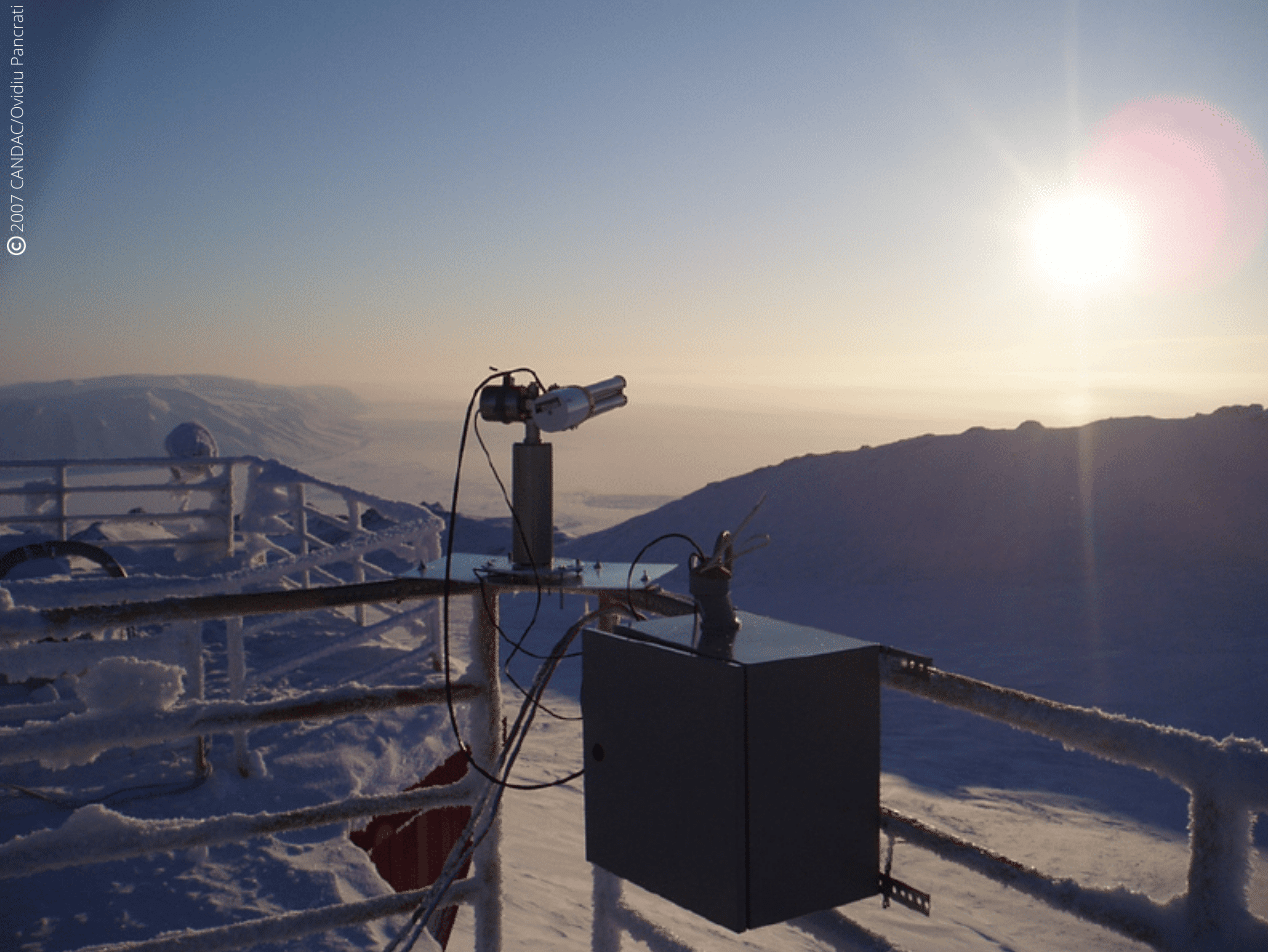
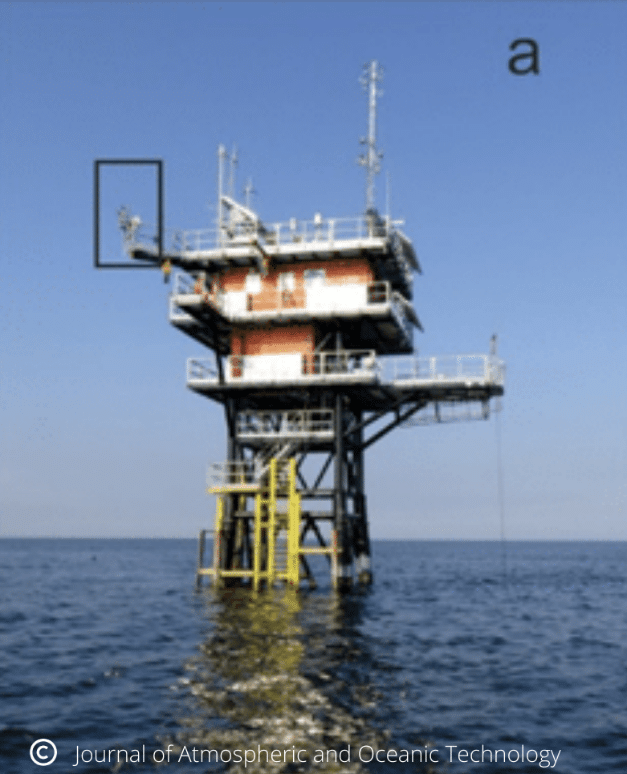
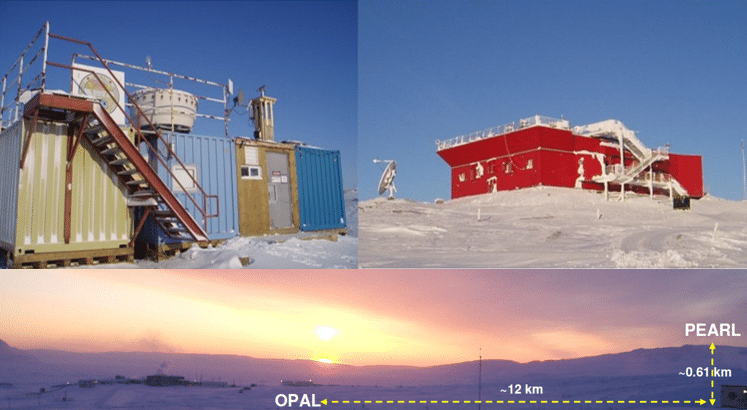
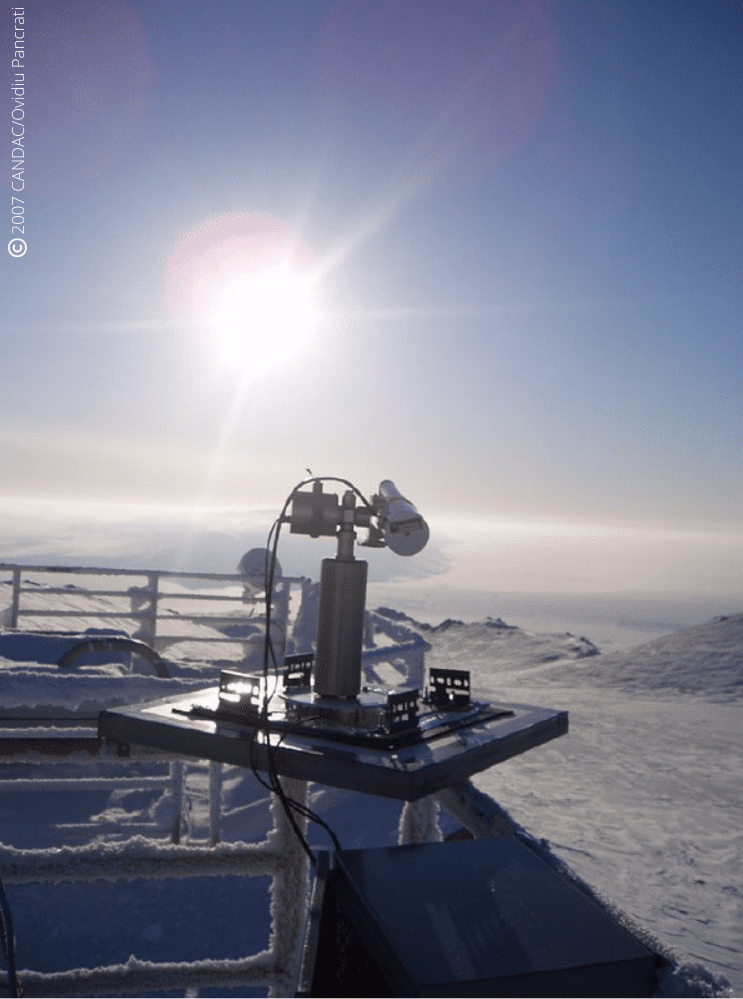
Pearl and Opal CE318-T photometers recording AOD and measurements in Canada’s high Arctic for AEROCAN.
Keywords : Aerosols, photometer, monitoring, Earth observation, remote sensing, CAL/VAL, Arctic.
March 23rd 2022
The Canadian Arctic is probably one of the best areas to conduct climatological studies, especially on global warming given the purity of the atmosphere in this zone, especially due to the absence of anthropological pollution.
Nevertheless, this rather hostile land, due to its temperatures, can make the difficulties of recording measurements very real. Consequently, there is a lack of measurements in the Arctic, hence the need to install platforms with robust and reliable measuring instruments.
Some of those platforms, especially PEARL and OPAL, have a particular emphasis on the Arctic because Canada has a significant portion of its territory in the Arctic.
The Polar Environmental Atmospheric Research Lab (PEARL) and the zerO altitude Polar Atmosphere Laboratory (OPAL) which is part of PEARL, is operated by the CAnadian Network for the Detection of Atmospheric Change (CANDAC) which is a member of AEROCAN. Formed in 2005, PEARL constitutes a network of universities and government researchers dedicated to studying the changing atmosphere over Canada.
The first task of PEARL was to renew and operate the existing laboratory at Eureka in Nunavut, which was created to contribute to the world-wide effort to intensively study the Arctic region through AEROCAN.
The AEROCAN photometer network is run as a joint collaboration between the Université de Sherbrooke and the Meteorological Service of Canada (MSC). It is a full-fledged sub-network of the much larger AERONET network of Cimel photometers and benefits from all the services that AERONET offers.
Objectives:
- Understanding atmospheric change over Canada
- Integration of measurements taken from space, aircraft, balloons and the ground
- Provision of quality-controlled research datasets to researchers
- Linkage with international networks for data exchange and supranational planning
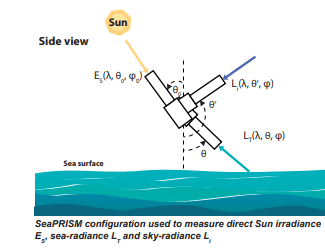
In addition, PEARL undertakes measurements that are simultaneous with those made by various satellite instruments. These “validation” measurements are extremely effective because of the location of PEARL and OPAL, and they further enhance the science return of the research as they use state-of-the-art technology solutions like the CE318-T Photometer.
PEARL is located at Eureka, Nunavut (80N, 86W) on Ellesmere Island in Canada’s high Arctic, 450 km north of Grise Fiord, the most northerly permanent settlement. This photometer site is 1,100 km from the North Pole. OPAL is located about 12 km southeast of the PEARL ridge lab which is at an elevation of 610 m. This dual placement was designed to study the layer between the two sites as well as provide an element of redundancy for the AOD measurements.

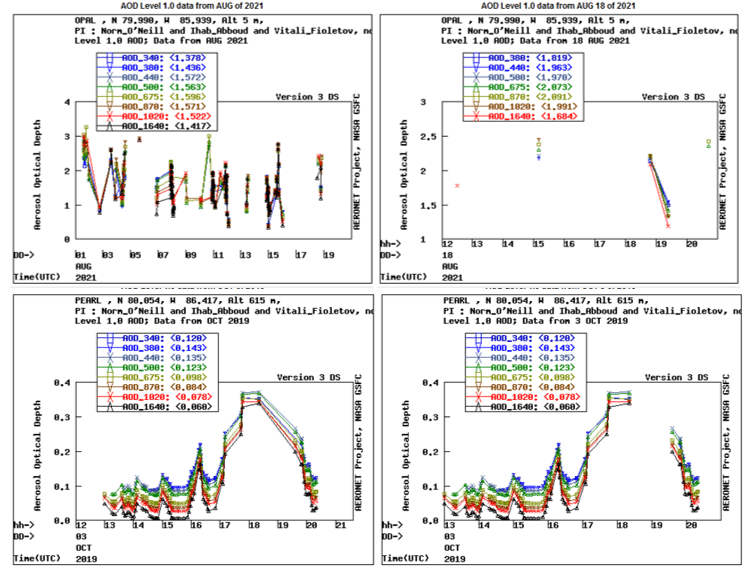
Results:
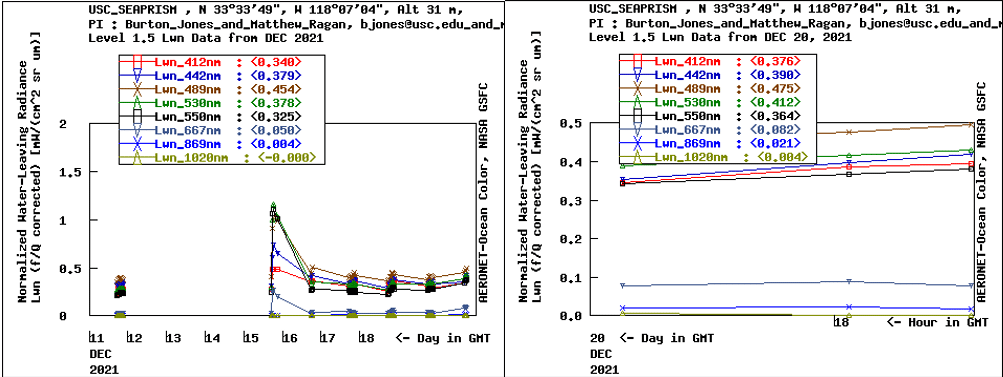
A multi-year AOD and effective radius climatology for the high Arctic showed a number of consistent features using the Cimel CE318-T Photometer:
• Spring to summer decrease of fine-mode AOD (probably attributable to biomass burning and/or anthropogenic pollution)
• Significant correlation of fine mode AOD with CO (Carbon monoxide) concentration which indicates a predominance of biomass burning aerosols throughout the entire year
• West to East decrease in AOD on a pan-Arctic scale
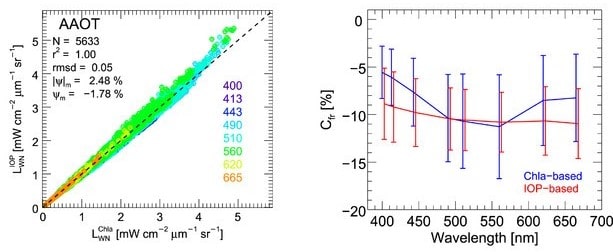
Another study (Antuña-Marrero et al., 2022) has been conducted for water vapor research.
It shows that it is feasible to use Cimel CE318-T Photometer AERONET observations in the Arctic for water vapor research, considering the robust quantification of its dry bias that has been established.
As a matter of fact, AERONET imposes standardization of instruments, calibration, processing and distribution that Cimel is the exclusive provider. Its IWV (Integrated Water Vapor) observations are an ideal standard dataset to re-calibrate or homogenize the rest of the instrumental IWV observations to a predefined absolute standard dataset.

References:
- Antuña-Marrero, Juan Carlos & Román, Roberto & Cachorro, Victoria & Mateos, David & Toledano, Carlos & Calle, Abel & Antuña Sánchez, Juan Carlos & Vaquero-Martínez, Javier & Antón, Manuel & Baraja, Ángel. (2022). Integrated water vapor over the Arctic: Comparison between radiosondes and sun photometer observations. Atmospheric Research. 270. 106059. 10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106059.
- AboEl‐Fetouh, Y., O’Neill, N. T., Ranjbar, K., Hesaraki, S., Abboud, I., & Sobolewski, P. S. (2020). Climatological‐scale analysis of intensive and semi‐intensive aerosol parameters derived from AERONET retrievals over the Arctic. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125, e2019JD031569. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031569
- Mölders, N. and Friberg, M. (2020) Using MAN and Coastal AERONET Measurements to Assess the Suitability of MODIS C6.1 Aerosol Optical Depth for Monitoring Changes from Increased Arctic Shipping. Open Journal of Air Pollution, 9, 77-104.
https://doi.org/10.4236/ojap.2020.94006